The Impact of AI on the Global Job Market



Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not just transforming industries—it’s reshaping the very nature of work. From automation of routine tasks to the creation of entirely new roles, the global job market is undergoing a major shift. This article examines how AI is influencing employment, the sectors most affected, the new opportunities it brings, and what this means for workers, businesses and policymakers.
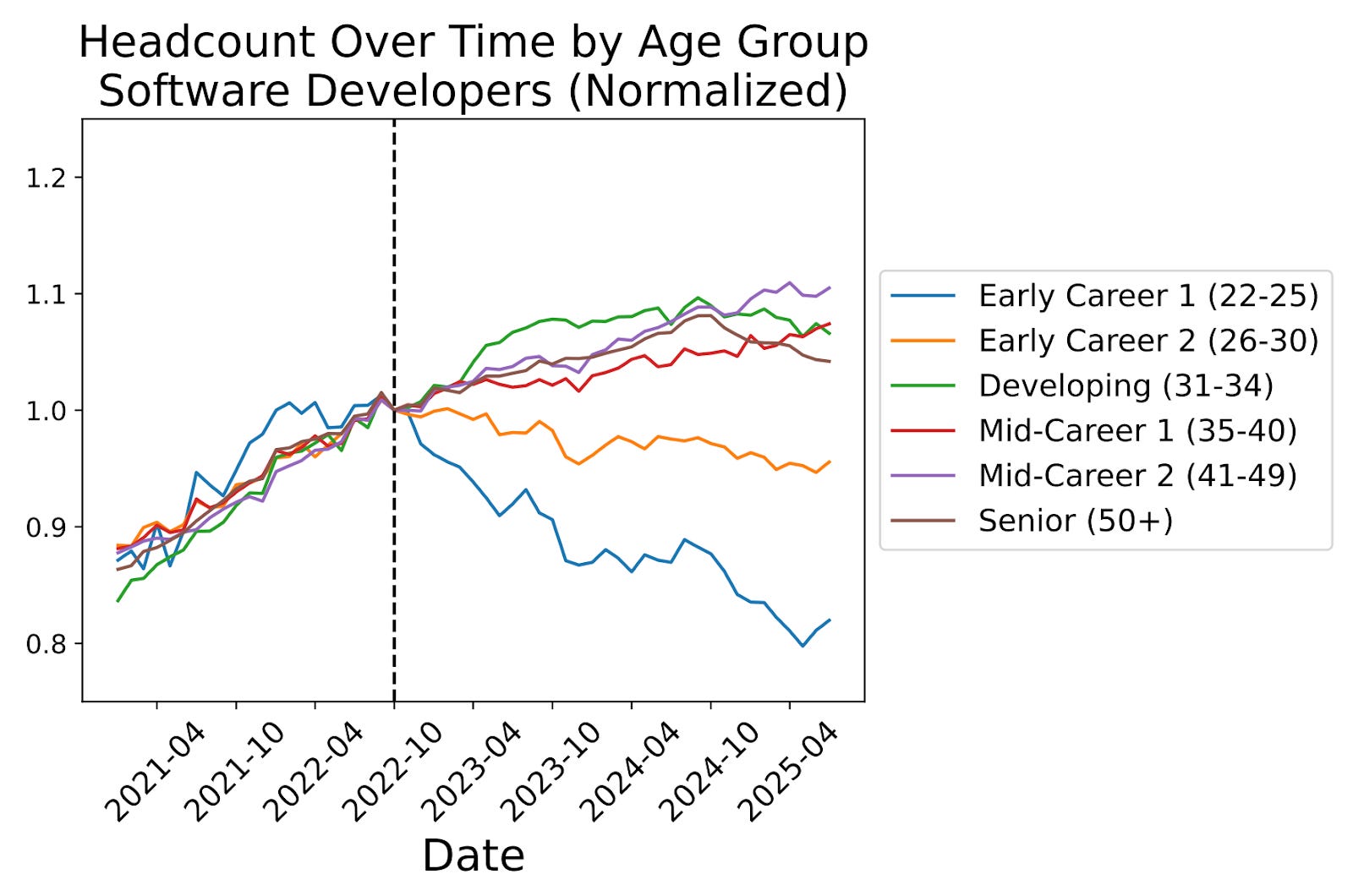
1. What the Data Shows
1.1 Scope of AI’s Impact
Various global studies estimate that a significant portion of jobs will be affected by AI in the coming years:
-
According to International Monetary Fund (IMF), roughly 40 % of jobs globally could be impacted, with up to 60 % in advanced economies. (جلف نيوز)
-
A report by PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC) finds that sectors most exposed to AI are seeing nearly 5× higher productivity growth than less-exposed sectors. (PwC)
-
Analyses show that jobs requiring AI-skills are growing faster: for example, job postings for AI-specialist skills are growing 3.5× faster than for all jobs. (PwC)
1.2 Displacement vs Creation
-
While some roles will be displaced or changed significantly, many experts emphasize that AI also creates new opportunities and jobs. For example, PwC notes that AI “has the potential to create more jobs than it displaces” if harnessed properly. (PwC)
-
Some sectors are already showing slowing job-growth in roles exposed to AI. For instance, J.P. Morgan found job-growth across certain white-collar tech industries turned ‘tepid’ post large-scale AI adoption. (جى بى مورجان)
2. Who & What Is Most Affected
2.1 High-Risk Roles & Sectors
-
Routine, repetitive tasks such as administrative support, data entry, legal assistants are among the higher risk categories. For example, one report estimated up to 46 % of U.S. administrative roles are exposed. (ذا ناشيونال)
-
Many knowledge-intensive roles in advanced economies are also exposed—counter to previous waves of automation which mostly impacted manual labour. (Khaleej Times)
2.2 Emerging Opportunities
-
Jobs requiring AI-related competencies (machine learning engineers, data scientists, AI ethics specialists) are in high demand and often carry a wage premium. (PwC)
-
Skills in adaptability, digital literacy, creativity, human-centric problem-solving are increasingly valuable as AI complements human work rather than purely replaces it.
-
Some reports suggest that businesses are now more focused on skill-based hiring rather than traditional degrees, especially for AI-exposed jobs. (arXiv)
3. Why This Matters (and Why Now)
-
Productivity gains: AI-intensive sectors are seeing much stronger productivity growth, which can drive economic expansion and higher living standards if managed well.
-
Skill shifts: The nature of what employers want is changing fast. Workers whose skills don’t evolve may find themselves at a disadvantage.
-
Inequality risks: Without careful policy and up-skilling efforts, AI’s benefits may accrue disproportionately to those in high-skill jobs or in advanced economies, widening gaps. The IMF warned about this very risk. (جلف نيوز)
-
Global competition: Countries and regions that build strong AI talent and infrastructure could gain competitive advantage, while others may lag.
4. Challenges & Considerations
-
Transition period: While new jobs are created, there may be a gap during which displaced workers struggle to find new roles or require reskilling.
-
Speed of change: With AI advancing fast, educational systems, training programs and labour policies may struggle to keep up.
-
Geographic and sectoral disparities: The impact of AI won’t be uniform—some countries, industries or roles will face greater risk or opportunity than others.
-
Definition of “job” changes: Many roles will evolve rather than disappear—requiring workers to change what they do rather than simply lose their job.
-
Ethical, regulatory, social aspects: As AI changes the nature of work, questions of fairness, worker rights, data privacy and governance become important.
5. Implications for Workers, Businesses & Your Context
-
For workers: It’s vital to stay adaptable—learn new skills, especially those complementary to AI (critical thinking, human creativity, judgement). Consider continuous learning and reskilling as part of your career strategy.
-
For businesses: Organisations should anticipate how AI will impact their workforce and operations—identify which roles will change, invest in training, and redesign workflows to leverage human + AI synergy.
-
For your context (e-commerce/store focus):
-
The skills you may prioritise in hiring (or training your team) are shifting: digital marketing, AI-assisted content creation, data analytics.
-
Some tasks (product descriptions, ad-copy generation, image generation, customer-chat automation) may be increasingly handled or assisted by AI—so consider how your business will adapt and leverage these tools to stay competitive.
-
Consider how to position your workforce and operations in a way that emphasises human strengths (e.g., customer insight, relationship building, local knowledge) alongside AI tools.
-
Conclusion
AI’s impact on the global job market is real, multifaceted and accelerating. While it presents risks—especially for roles with routine, repetitive or narrowly defined tasks—it also opens up significant opportunities for new kinds of work, productivity gains and economic growth. The difference will lie in how individuals, organisations and societies adapt: through upskilling, thoughtful deployment of AI, and policies that ensure the benefits are broadly shared.
For workers and business owners alike, the message is clear: “change is not optional—it’s inevitable.” Embrace the opportunity to be part of the transformation, rather than be left behind.
Sources
-
“How Will AI Affect the Global Workforce?” – Goldman Sachs Research. (goldmansachs.com)
-
“AI-exposed sectors experience productivity surge as AI jobs climb and see up to 25% wage premium” – PwC 2024 Global AI Jobs Barometer. (PwC)
-
“AI will affect almost 40% jobs globally and worsen inequality” – Gulf News (IMF summary). (جلف نيوز)
-
“Is AI already impacting job growth?” – J.P. Morgan Global Research. (جى بى مورجان)
-
“Skills or Degree? The Rise of Skill-Based Hiring for AI and Green Jobs.” (Academic study) (arXiv)
If you li
